Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. There are several different types of diabetes, each with its own unique characteristics and treatment approaches.
By understanding the different types of diabetes, you can better manage your condition and make informed decisions about your health. In this guide, we will explore the various types of diabetes and provide you with the knowledge you need to take control of your health.
Type 1 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options.
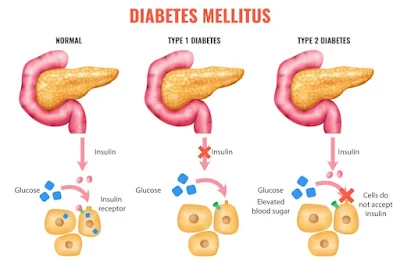
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This results in a lack of insulin, a hormone that is necessary for the body to regulate blood sugar levels. The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, extreme hunger, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, type 1 diabetes can lead to serious complications such as heart disease, kidney damage, and nerve damage.
The main treatment for type 1 diabetes is insulin therapy, which involves injecting insulin into the body to replace the insulin that is no longer being produced. This helps to regulate blood sugar levels and prevent complications. In addition to insulin therapy, people with type 1 diabetes may also need to monitor their blood sugar levels, follow a healthy diet, engage in regular physical activity, and take other medications to manage their condition.
It is important for individuals with type 1 diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a personalized treatment plan and to regularly monitor their blood sugar levels. With proper management and care, people with type 1 diabetes can live healthy and fulfilling lives.
Type 2 Diabetes: Risk Factors, Prevention, and Management Strategies.
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects the way the body processes glucose, or sugar. Unlike type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease, type 2 diabetes is often caused by lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of physical activity, and poor diet.
Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being over the age of 45, and being of certain ethnic backgrounds, such as African American, Hispanic, or Asian.
Prevention of type 2 diabetes involves making healthy lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and avoiding tobacco use. It is also important to manage other health conditions, such as high blood pressure and high cholesterol, as these can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
For those who already have type 2 diabetes, management strategies include monitoring blood sugar levels, taking prescribed medications, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress. It is important to work closely with a healthcare team to develop an individualized treatment plan and to regularly monitor and manage the condition.
By understanding the different types of diabetes and implementing appropriate prevention and management strategies, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Gestational Diabetes: Causes, Risks, and Pregnancy Management.
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that develop during pregnancy and usually resolve after giving birth.
The exact cause of gestational diabetes is unknown, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy. The placenta produces hormones that can interfere with the body's ability to use insulin effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels.
Women who are overweight or obese, have a family history of diabetes, have had gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy, or are older than 25 are at a higher risk of developing gestational diabetes.
Gestational diabetes can have risks for both the mother and the baby. For the mother, it can increase the risk of high blood pressure, preeclampsia, and the need for a cesarean delivery. For the baby, it can increase the risk of macrosomia (a larger than average baby), low blood sugar levels after birth, and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Managing gestational diabetes involves monitoring blood sugar levels, following a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and, in some cases, taking insulin or other medications. It is important for pregnant women with gestational diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to ensure the best possible outcomes for both themselves and their babies.
Prediabetes: Identifying the Warning Signs and Preventing Progression.
Prediabetes is a condition in which blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. It is often considered a warning sign that a person is at risk for developing diabetes in the future.
The exact cause of prediabetes is not known, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. People who are overweight or obese, have a family history of diabetes, have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, or are physically inactive are at a higher risk of developing prediabetes.
There are often no symptoms of prediabetes, which is why it is important to get regular check-ups and blood tests to monitor blood sugar levels. If left untreated, prediabetes can progress to type 2 diabetes, which can lead to serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage.
Fortunately, prediabetes can often be reversed or prevented through lifestyle changes. These include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet that is low in sugar and refined carbohydrates, engaging in regular physical activity, and quitting smoking if applicable. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to help manage blood sugar levels.
By identifying the warning signs of prediabetes and taking proactive steps to prevent its progression, individuals can reduce their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and improve their overall health and well-being. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance.
Other Types of Diabetes: Exploring Less Common Forms and Their Implications.
In addition to type 2 diabetes and prediabetes, there are several other less common forms of diabetes that individuals may be diagnosed with. These include type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and monogenic diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. This form of diabetes typically develops in childhood or adolescence, although it can occur at any age. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy to manage their blood sugar levels.
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and affects approximately 2-10% of pregnant women. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that develop or are first recognized during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, but women who have had gestational diabetes are at an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
Monogenic diabetes is a rare form of diabetes that is caused by a mutation in a single gene. This type of diabetes is often diagnosed in childhood or early adulthood and can be mistaken for type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Treatment for monogenic diabetes varies depending on the specific genetic mutation involved.
Understanding the different types of diabetes is important for individuals to effectively manage their condition and make informed decisions about their health. It is recommended that individuals with diabetes work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals.





Comments
Post a Comment